Top 10 Foods High in Vitamin A

Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for good vision, immune system function, and healthy skin. (1,2)
A deficiency of vitamin A can lead to blindness and increased viral infection. However, vitamin A deficiency is mainly considered a problem in developing countries, where it is a leading cause of blindness in children. (3,4)
About The Types of Vitamin A and Retinol Equivalents
- Vitamin A is available to humans in 2 ways: preformed vitamin A and carotenoids. (1)
- Carotenoids, like beta-carotene, are found in plant foods and have to be converted by the body into vitamin A. (1,5)
- Preformed vitamin A is found in animal food sources like liver, meat, fish, and dairy. Like carotenoids, the preformed vitamin A also needs to be metabolized by the body into an active form of vitamin A. (1)
- In rare cases certain people cannot convert carotenoids to vitamin A and should consume vitamin A from animal food sources or supplements. These people should see our lists of meats high in vitamin A, fish high in vitamin A, and dairy foods high in vitamin A.
- Since vitamin A comes in many forms, starting in July 2018 large US food producers will report vitamin A values in retinol activity equivalents (RAE) of vitamin A. The new daily value for Vitamin A RAE will be 900mcg per day. (6)
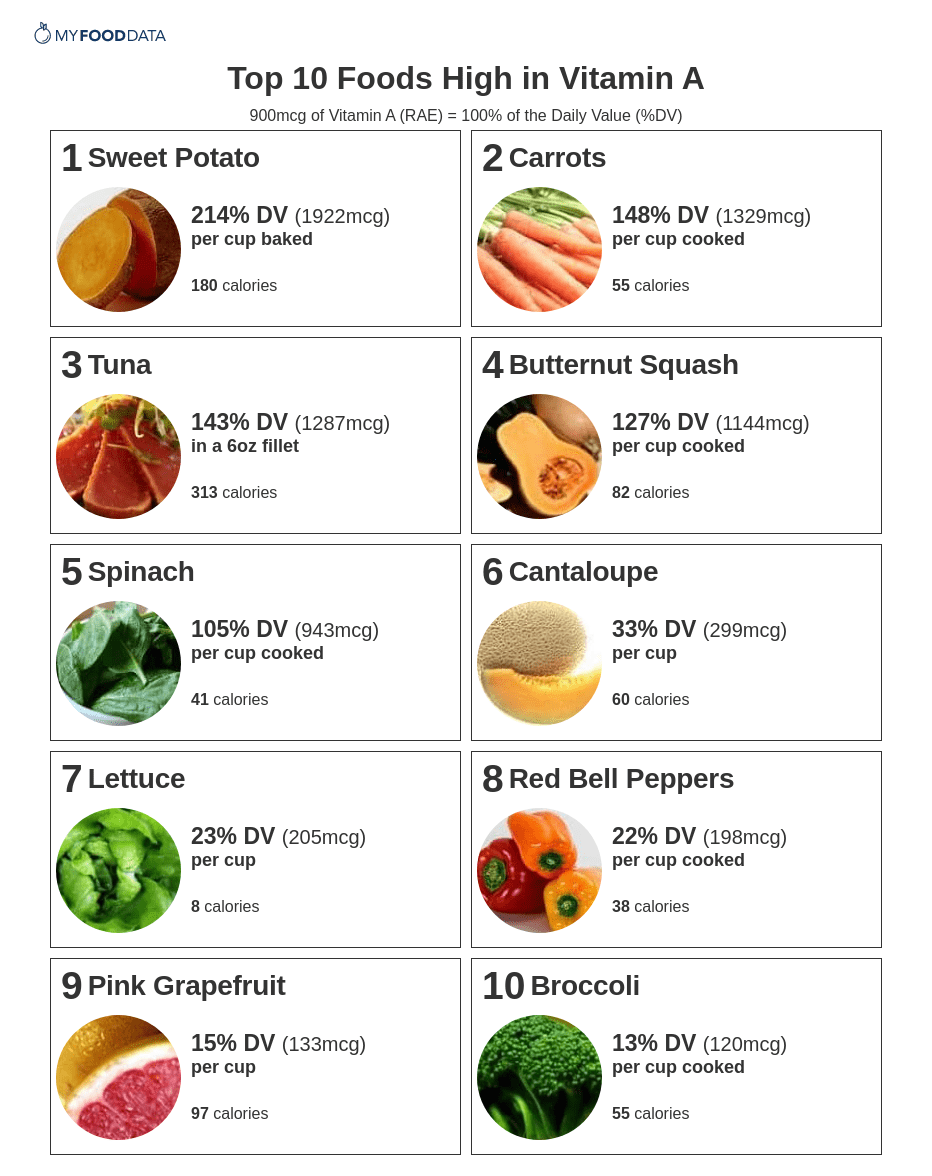
High vitamin A foods include sweet potatoes, carrots, fish (tuna), winter squashes, dark leafy greens, cantaloupe, lettuce, bell peppers, pink grapefruit, and broccoli. The current daily value (DV) for Vitamin A is 900mcg of retinol activity equivalents (RAEs). (6)
Below is a list of foods high in vitamin A.
Foods High In Vitamin A
-
1. Sweet Potato + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup BakedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories1922mcg
(214% DV)961mcg
(107% DV)2136mcg
(237% DV)A medium-sized baked sweet potato provides 122% DV of vitamin A.
-
 2. Carrots + Add
2. Carrots + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup CookedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories1329mcg
(148% DV)852mcg
(95% DV)4869mcg
(541% DV)A medium-sized carrot provides 44% DV of vitamin A.
-
 3. Tuna + Add
3. Tuna + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
in a 6oz FilletVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories1287mcg
(143% DV)757mcg
(84% DV)823mcg
(91% DV)Other Fish and Seafood High in Vitamin A
- 201% DV in a 5.5 oz fillet of eel
- 150% DV in 1 tsp of cod liver oil
- 36% DV in 20 small clams
- 24% DV in 3oz of cooked mackerel
See the complete list of fish high in vitamin A.
-
 4. Butternut Squash + Add
4. Butternut Squash + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup CookedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories1144mcg
(127% DV)558mcg
(62% DV)2790mcg
(310% DV)Other Squash High in Vitamin A
- 212% DV in 1 cup of canned pumpkin
- 76% DV in 1 cup of hubbard squash
- 59% DV per cup of average winter squash
- 11% DV per cup of acorn squash
See the full list of vegetables high in vitamin A.
-
 5. Spinach + Add
5. Spinach + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup CookedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories943mcg
(105% DV)524mcg
(58% DV)4557mcg
(506% DV)Other Dark Leafy Greens High in vitamin A
- 98% DV per cup of cooked kale
- 96% DV per cup of cooked mustard greens
- 80% DV per cup of cooked collards
- 60% DV per cup of cooked Swiss chard
- 40% DV per cup of cooked bok choy
See the full list of vegetables high in vitamin A.
-
6. Cantaloupe + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per CupVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories299mcg
(33% DV)169mcg
(19% DV)994mcg
(110% DV)Other Fruits High in Vitamin A
- 17% DV in 1 cup of apricots
- 10% DV per cup of sliced mango
- 8% DV per cup of sliced papaya
See the full list of fruits high in vitamin A.
-
7. Lettuce + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per CupVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories205mcg
(23% DV)436mcg
(48% DV)5129mcg
(570% DV) -
 8. Red Bell Peppers + Add
8. Red Bell Peppers + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup CookedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories198mcg
(22% DV)147mcg
(16% DV)1050mcg
(117% DV)Cooked Green Bell Peppers provide 3% DV of Vitamin A per cup cooked.
-
 9. Pink Grapefruit + Add
9. Pink Grapefruit + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per CupVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories133mcg
(15% DV)58mcg
(6% DV)276mcg
(31% DV)Note: Pink grapefruit provides about 30 times more vitamin A than white grapefruit. View the complete nutrition comparison of pink vs white grapefruit.
-
 10. Broccoli + Add
10. Broccoli + Add
Vitamin A (RAE)
per Cup CookedVitamin A (RAE)
per 100gVitamin A (RAE)
per 200 Calories120mcg
(13% DV)77mcg
(9% DV)440mcg
(49% DV)
Printable One Page Sheet
Vitamin A Foods by Nutrient Density (Vitamin A per Gram)
| Food | Serving | Vitamin A (RAE) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Cod Liver Oil + | 100 grams | 3333% DV (30000mcg) |
| 2. Beef Liver (Cooked) + | 100 grams | 860% DV (7744mcg) |
| 3. Fortified Breakfast Cereals + | 100 grams | 110% DV (990mcg) |
| 4. Baked Sweet Potatoes + | 100 grams | 107% DV (961mcg) |
| 5. Cooked Carrots + | 100 grams | 95% DV (852mcg) |
| 6. Bluefin Tuna (Raw or Cooked) + | 100 grams | 84% DV (757mcg) |
| 7. Butter + | 100 grams | 76% DV (684mcg) |
| 8. Dried Apricots + | 100 grams | 70% DV (633mcg) |
| 9. Raw Turnip Greens + | 100 grams | 64% DV (579mcg) |
| 10. Cooked Spinach + | 100 grams | 58% DV (524mcg) |
Other Vitamin A Rich Foods
| Food | Serving | Vitamin A (RAE) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Cooked Lamb Liver + | 3oz | 735% DV (6615mcg) |
| 2. Cooked Eel + | per 5.5oz fillet | 201% DV (1808mcg) |
| 3. Cooked Chicken Liver + | per liver (44g) | 195% DV (1752mcg) |
| 4. Light Whipping Cream + | per cup whipped | 37% DV (335mcg) |
| 5. Cooked Garden Cress + | per cup | 35% DV (313mcg) |
| 6. Chocolate Mousse + | 1/2 cup | 31% DV (283mcg) |
| 7. Rose Hips + | per cup | 31% DV (276mcg) |
| 8. Raw Parsley + | per cup chopped | 28% DV (253mcg) |
| 9. Smoked Sturgeon + | per 3oz | 26% DV (238mcg) |
| 10. Cooked Jute Potherb (Molokhiya) + | per cup | 25% DV (225mcg) |
| 11. Whole Milk + | per 16oz cup | 25% DV (224mcg) |
| 12. Minestrone + | per cup | 24% DV (214mcg) |
| 13. Ricotta Cheese + | per 1/2 cup | 17% DV (149mcg) |
| 14. Farmed Salmon (Cooked) + | per 6oz fillet | 13% DV (117mcg) |
| 15. Eggs + | 1 large egg (90g) | 11% DV (101mcg) |
| 16. Canned Oysters + | per 12oz can | 9% DV (77mcg) |
| 17. Tangerines + | per cup sections | 7% DV (66mcg) |
| 18. Plain Whole Milk Yogurt + | per cup | 7% DV (66mcg) |
Vitamin A Requirements By Age and Gender
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Vitamin A ranges from 300mcg to 1300mcg per day. The daily value for vitamin A is 900mcg per day. (6)
| Life Stage | RDA |
|---|---|
| Infants* | |
| 0-6 months old | 400mcg |
| 7-12 months old | 500mcg |
| Children | |
| 1-3 years old | 300mcg |
| 4-8 years old | 400mcg |
| Males | |
| 9-13 years old | 600mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 900mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 900mcg |
| 50+ years old | 900mcg |
| Females | |
| 9-13 years old | 600mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 700mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 700mcg |
| 50+ years old | 700mcg |
| Pregnancy | |
| 14-18 years old | 750mcg |
| 18+ years old | 770mcg |
| Lactation | |
| 14-18 years old | 1200mcg |
| 18+ years old | 1300mcg |
Source: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A.
From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Foods Low in Vitamin A, RAE
- Vegetables High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Fruits High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Vegetarian Foods High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Nuts High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Dairy High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin A, RAE
- Fast Foods High in Vitamin A, RAE
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Hodge C, Taylor C. Vitamin A 2023 Jan 2. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. 33620821
- De Flora S, Bagnasco M, Vainio H. The importance of vitamin A in nutrition Mutagenesis. 1999 Mar;14(2):153-72. doi: 10.1093/mutage/14.2.153. 10229917
- DeMaeyer EM. The vicious cycle of vitamin a deficiency: A review Nutr Health. 1986;4(2):105-12. doi: 10.1177/026010608600400206. 3090484
- Strobel M, Tinz J, Biesalski HK. Vitamin A Deficiency Eur J Nutr. 2007 Jul;46 Suppl 1:I1-20. doi: 10.1007/s00394-007-1001-z. 17665093
- Weber D, Grune T. Beta-carotene is an important vitamin A source for humans Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Feb;56(2):251-8. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100230. Epub 2011 Sep 29. 21957049
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
Simplify Nutrition Tracking with MyFoodData!
Speedy Tools and Detailed Data FREEEasily analyze your meals to find the best foods for your goals.
✅ Use our recipe nutrition calculator and nutrition comparison tool.
✅ Access expert nutrition data tools and in-depth articles.
✅ Log foods and organize your recipes with a free account.


 Next ➞
Next ➞
