Vegetables High in Copper

Vegetables comprise some of the most nutrient dense foods in our diets and copper is one of the many important nutrients they contain.
Copper is an essential nutrient, and is necessary for a variety of functions throughout the body, including energy production, iron transport, nervous system function, cholesterol metabolism, bone and connective tissue production, and immune system function. (1)
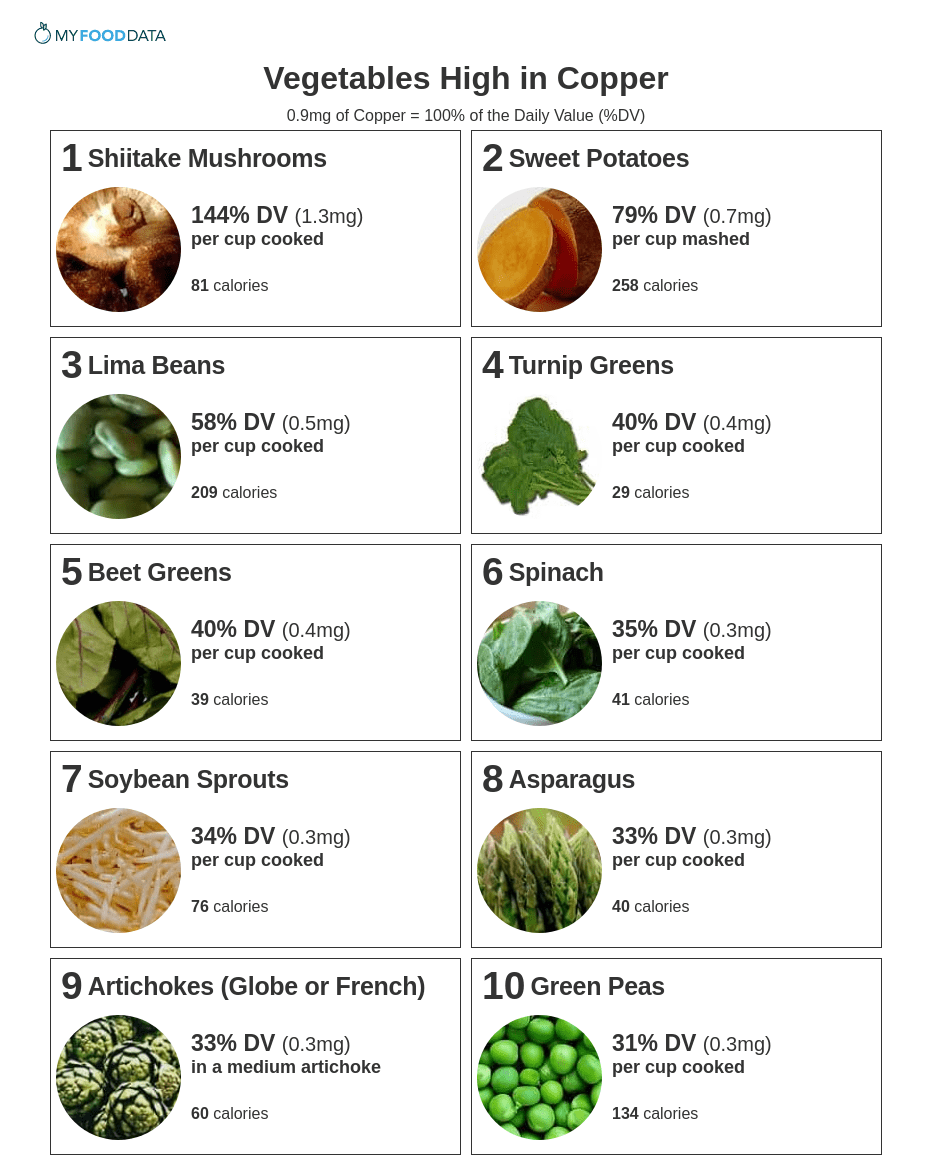
Vegetables high in copper include mushrooms, sweet potatoes, lima beans, turnip greens, beet greens, spinach, soybean sprouts, asparagus, artichokes, and green peas. The current daily value (DV) for copper is 0.9mg. (2)
For more high copper vegetables see the extended list of less common vegetables rich in copper.
List of Vegetables High in Copper
-
 1. Shiitake Mushrooms + Add
1. Shiitake Mushrooms + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories1.3mg
(144% DV)0.9mg
(100% DV)3.2mg
(356% DV)More Mushrooms High in Copper
- 87% DV in 1 cup of white button mushrooms
- 52% DV in 1 cup of portobellos
- 48% DV in 1 cup of cremini mushrooms
- 46% DV in 1 cup of morels
- 41% DV in 1 cup of canned mushrooms
-
 2. Sweet Potatoes + Add
2. Sweet Potatoes + Add
Copper
per Cup MashedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.7mg
(79% DV)0.3mg
(31% DV)0.6mg
(61% DV)- 37% DV in a baked potato
-
 3. Lima Beans + Add
3. Lima Beans + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.5mg
(58% DV)0.3mg
(34% DV)0.5mg
(55% DV) -
 4. Turnip Greens + Add
4. Turnip Greens + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.4mg
(40% DV)0.3mg
(28% DV)2.5mg
(281% DV) -
 5. Beet Greens + Add
5. Beet Greens + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.4mg
(40% DV)0.3mg
(28% DV)1.9mg
(207% DV) -
 6. Spinach + Add
6. Spinach + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.3mg
(35% DV)0.2mg
(19% DV)1.5mg
(168% DV)Other Leafy Greens High in Copper
- 32% DV in 1 cup of Swiss chard
- 27% DV in 1 cup of kale
- 23% DV in 1 cup of mustard greens
-
 7. Soybean Sprouts + Add
7. Soybean Sprouts + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.3mg
(34% DV)0.3mg
(37% DV)0.8mg
(91% DV)More Sprouts High in Copper
- 37% DV in 1 cup of lentil sprouts
- 36% DV in 1 cup of pea sprouts
- 22% DV in 1 cup of mung bean sprouts
-
 8. Asparagus + Add
8. Asparagus + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.3mg
(33% DV)0.2mg
(18% DV)1.5mg
(167% DV) -
 9. Artichokes (Globe or French) + Add
9. Artichokes (Globe or French) + Add
Copper
in a Medium ArtichokeCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.3mg
(33% DV)0.2mg
(26% DV)1mg
(109% DV) -
 10. Green Peas + Add
10. Green Peas + Add
Copper
per Cup CookedCopper
per 100gCopper
per 200 Calories0.3mg
(31% DV)0.2mg
(19% DV)0.4mg
(46% DV)
Printable One Page Sheet
Less Common Copper Rich Vegetables
| Food | Serving | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Canned Tomato Puree + | per cup | 80% DV (0.7mg) |
| 2. Yautia + | per cup | 39% DV (0.3mg) |
| 3. Pickled Beets + | per cup | 29% DV (0.3mg) |
| 4. Pumpkin + | per cup cooked | 25% DV (0.2mg) |
| 5. Jute Potherb (Molokhiya) + | per cup cooked | 25% DV (0.2mg) |
| 6. Kohlrabi + | per cup cooked | 24% DV (0.2mg) |
| 7. Lotus Root + | per 10 slices | 23% DV (0.2mg) |
| 8. Canned Palm Hearts + | per cup | 22% DV (0.2mg) |
| 9. Taro + | per cup | 20% DV (0.2mg) |
| 10. Acorn Squash + | per cup cooked | 20% DV (0.2mg) |
| 11. Chayote + | per cup cooked | 20% DV (0.2mg) |
Copper Requirements By Age and Gender
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for copper ranges from 330mcg (0.33mg) to 1000mcg (1mg) per day, depending on a person's age and gender. The daily value (DV) for copper is 0.9mg (900mcg) per day. The daily value is a general guideline that will prevent nutrient deficiency for most people and is listed on food labels, while the RDA is specific for particular groups of people. (2)
Note: 1mg = 1000mcg (micrograms)
| Life Stage | RDA |
|---|---|
| Infants* | |
| 0-6 months old | 200mcg (micrograms) |
| 7-12 months old | 220mcg (micrograms) |
| Children | |
| 1-3 years old | 340mcg |
| 4-8 years old | 440mcg |
| Males | |
| 9-13 years old | 700mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 890mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 900mcg |
| 50+ years old | 900mcg |
| Females | |
| 9-13 years old | 700mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 890mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 900mcg |
| 50+ years old | 900mcg |
| Pregnancy | |
| 14-18 years old | 1000mcg |
| 18+ years old | 1000mcg |
| Lactation | |
| 14-18 years old | 985mcg |
| 18+ years old | 1000mcg |
Source: Dietary Reference Intakes for Copper.
From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Copper
- Foods Low in Copper
- Vegetables High in Copper
- Fruits High in Copper
- Vegetarian Foods High in Copper
- Nuts High in Copper
- Grains High in Copper
- Beans High in Copper
- Dairy High in Copper
- Breakfast Cereals High in Copper
- Fast Foods High in Copper
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Kumar P, Hamza N, Madhok B, De Alwis N, Sharma M, Miras AD, Mahawar KK. Copper Deficiency: Causes, Manifestations, and Treatment Obes Surg. 2016 Jun;26(6):1335-42. doi: 10.1007/s11695-016-2162-8. 27034062
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
Simplify Nutrition Tracking with MyFoodData!
Speedy Tools and Detailed Data FREEEasily analyze your meals to find the best foods for your goals.
✅ Use our recipe nutrition calculator and nutrition comparison tool.
✅ Access expert nutrition data tools and in-depth articles.
✅ Log foods and organize your recipes with a free account.


 Next ➞
Next ➞
