Fruits and Vegetables High in Iron

Iron is an essential mineral used to transport oxygen around the body in the form of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. A deficiency of iron causes anemia (low red blood cell count, leading to symptoms like fatigue and weakness), and a chronic deficiency can lead to organ failure. (1,2)
Contrary to popular belief, fruits and vegetables can be a good source of iron. In addition, vitamin C is abundant in fruits and vegetables and helps increase the absorption of iron into the body. (3,4)
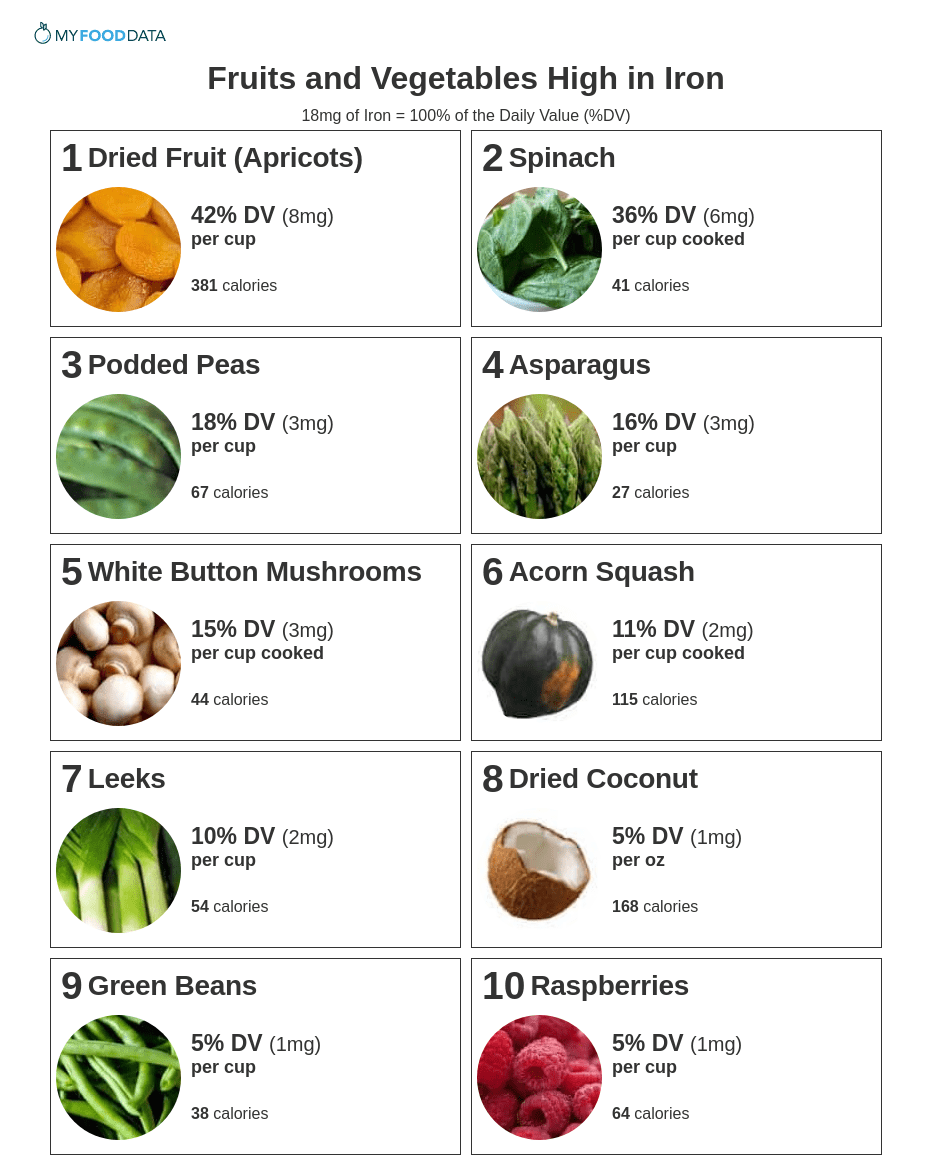
Fruits and vegetables high in iron include dried fruits, dark leafy greens, podded peas, asparagus, button mushrooms, acorn squash, leeks, dried coconut, green beans, and raspberries. The current daily value (DV) for iron is 18 milligrams (mg). (5)
Below is a list of fruits and vegetables high in iron, for more, see the extended list of iron rich fruits and vegetables, and the top 10 vegetarian foods highest in iron.
List of Fruits and Vegetables High in Iron
-
 1. Dried Fruit (Apricots) + Add
1. Dried Fruit (Apricots) + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories8mg
(42% DV)6mg
(35% DV)4mg
(22% DV)More Dried fruit High in Iron
- 36% DV per cup of dried peaches
- 26% DV per cup of dried prunes and currants
- 24% DV per cup of dried raisins
- 21% DV per cup of dried pears
- 17% DV per cup of dried figs
- 7% DV per cup of dried apples
Note: Dried fruit is high in natural sugars, so should be eaten in moderate servings of around 1 handful per day.
-
 2. Spinach + Add
2. Spinach + Add
Iron
per Cup CookedIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories6mg
(36% DV)4mg
(20% DV)31mg
(172% DV)Other Greens High in Iron
- 22% DV per cup of cooked Swiss chard
- 16% DV per cup of cooked turnip greens
- 6% DV per cup of raw chopped kale
- 5% DV per cup of raw chopped beet greens
-
 3. Podded Peas + Add
3. Podded Peas + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories3mg
(18% DV)2mg
(11% DV)9mg
(52% DV)- Lima beans provide 23% DV of iron per cup
-
 4. Asparagus + Add
4. Asparagus + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories3mg
(16% DV)2mg
(12% DV)21mg
(119% DV)A cup of asparagus contains just 27 calories.
-
 5. White Button Mushrooms + Add
5. White Button Mushrooms + Add
Iron
per Cup CookedIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories3mg
(15% DV)2mg
(10% DV)12mg
(69% DV)Other Mushrooms High in Iron
- 45% DV per cup of cooked morels
- 6% DV per cup of cooked oyster mushrooms
- 3% DV per cup of shiitake
-
 6. Acorn Squash + Add
6. Acorn Squash + Add
Iron
per Cup CookedIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories2mg
(11% DV)1mg
(5% DV)3mg
(18% DV)Pumpkin provides 7% DV per cup, most other winter squash provide 6% DV per cup.
-
 7. Leeks + Add
7. Leeks + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories2mg
(10% DV)2mg
(12% DV)7mg
(38% DV)Scallions (spring onions) are also high in iron with (2% DV) per onion.
-
 8. Dried Coconut + Add
8. Dried Coconut + Add
Iron
per OzIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories1mg
(5% DV)3mg
(19% DV)1mg
(6% DV)Other Coconut Products High in Iron
- 5% DV per ounce of toasted desiccated (dried) coconut
- 5% DV per ounce of creamed coconut
- 5% DV per ounce of coconut milk
-
 9. Green Beans + Add
9. Green Beans + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories1mg
(5% DV)1mg
(4% DV)5mg
(26% DV)See more vegetarian foods high in iron.
-
 10. Raspberries + Add
10. Raspberries + Add
Iron
per CupIron
per 100gIron
per 200 Calories1mg
(5% DV)1mg
(4% DV)3mg
(15% DV)Other Berries High in Iron
- 14% DV per cup of Mulberries
- 13% DV per cup of Elderberries
- 9% DV per cup of Raspberries
- 7% DV per cup of Blackberries
- 6% DV per cup of Strawberries
- 5% DV per cup of Raspberries
- 5% DV per cup of Blackberries
- 5% DV per cup of Longanberries
- 5% DV per cup of Wild Blueberries
Printable One Page Sheet
Even More Iron Rich Fruits and Vegetables
| Food | Serving | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Lemon Grass (Citronella) + | 1 cup | 30% DV (5mg) |
| 2. Palm Hearts + | 1 cup | 25% DV (5mg) |
| 3. Passion-Fruit (Granadilla) + | per cup | 21% DV (4mg) |
| 4. Parsley + | per cup | 21% DV (4mg) |
| 5. Succotash + | 1 cup | 16% DV (3mg) |
| 6. Horned Melon (Kiwano) + | 1 cup | 15% DV (3mg) |
| 7. Lentil Sprouts + | per cup cooked | 14% DV (2mg) |
| 8. Sauerkraut + | 1 cup | 12% DV (2mg) |
| 9. Dandelion Greens + | per cup | 9% DV (2mg) |
| 10. Artichokes (Globe or French) + | in a medium artichoke | 9% DV (2mg) |
| 11. Groundcherries + | 1 cup | 8% DV (1mg) |
| 12. Mamey Sapote + | 1 cup chopped | 8% DV (1mg) |
| 13. Avocados + | per Avocado | 6% DV (1mg) |
| 14. Lettuce + | per cup | 4% DV (1mg) |
| 15. Olives + | 1 large | 3% DV (0mg) |
From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Iron
- Foods Low in Iron
- Vegetables High in Iron
- Fruits High in Iron
- Vegetarian Foods High in Iron
- Nuts High in Iron
- Grains High in Iron
- Beans High in Iron
- Dairy High in Iron
- Breakfast Cereals High in Iron
- Fast Foods High in Iron
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Uniyal N, Sethi Y, Chopra H, Dhawan M, Emran TB. Iron deficiency Int J Surg. 2022 Sep;105:106871. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106871. Epub 2022 Aug 29. 36049619
- Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Iron Deficiency Anemia: An Updated Review Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. 36321557
- Ahmed F, Hasan N, Kabir Y. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Their Association With the Indicators of Iron and Inflammation Status Among Adolescent Girls Eur J Clin Nutr. 1997 Oct;51(10):698-702. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600469. 9347291
- Monsen ER. The role of vitamin C in iron absorption J Am Diet Assoc. 1988 Jul;88(7):786-90. 3290310
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
Simplify Nutrition Tracking with MyFoodData!
Speedy Tools and Detailed Data FREEEasily analyze your meals to find the best foods for your goals.
✅ Use our recipe nutrition calculator and nutrition comparison tool.
✅ Access expert nutrition data tools and in-depth articles.
✅ Log foods and organize your recipes with a free account.


 Next ➞
Next ➞
