Top 10 Vegetables Highest in Protein

Proteins are an important building block for all living things, and have many essential functions in the human body. This is why getting enough protein in your diet is crucial for good health.
Although many people think of meat when looking for protein sources, the truth is that many plant foods, including some vegetables, also have high levels of protein.
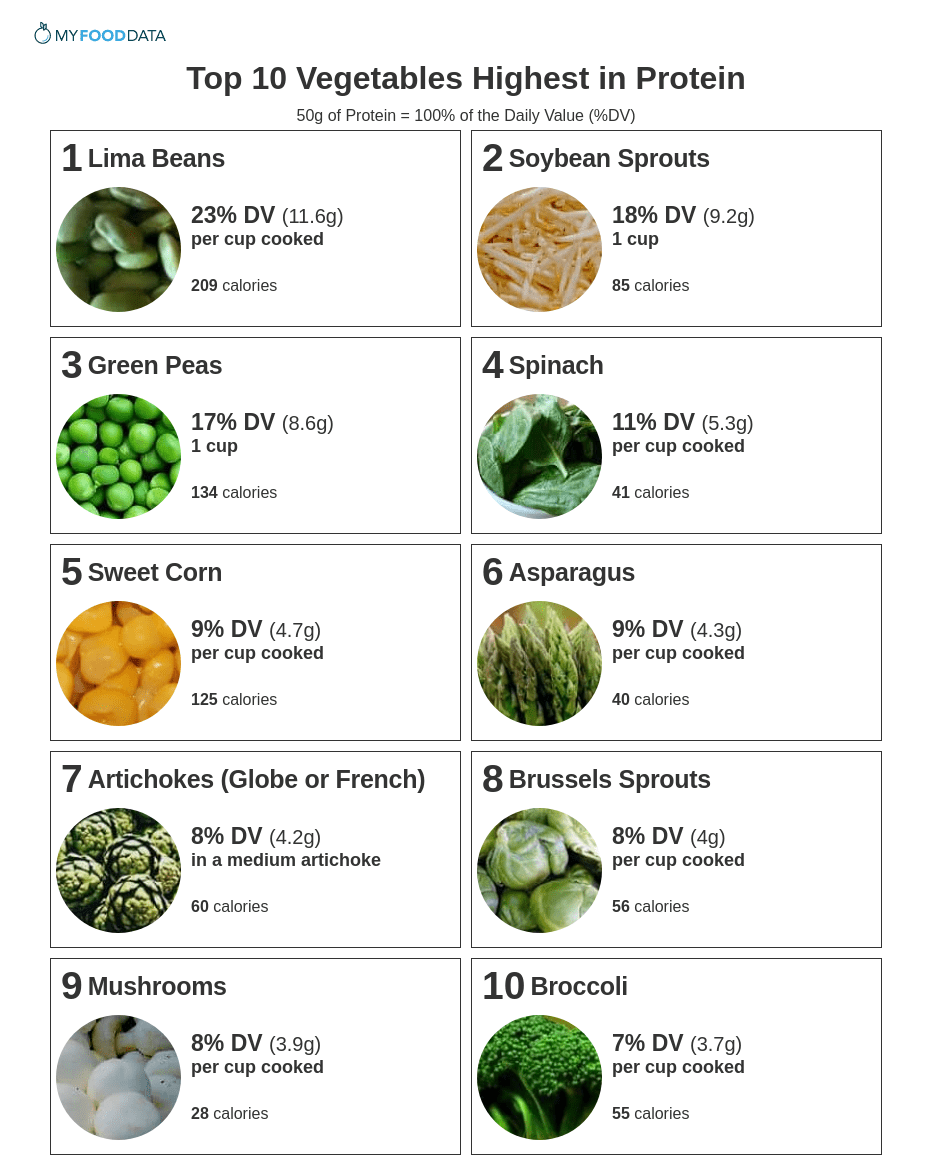
The current daily value (DV) for protein is 50 grams per day and is a target meant for most people. (1) Vegetables high in protein include lima beans, bean sprouts, green peas, spinach, sweet corn, asparagus, artichokes, brussels sprouts, mushrooms, and broccoli.
For more vegetarian and vegan sources of protein see the articles on beans and legumes highest in protein, and grains high in protein, and high protein nuts.
You can also see the uncurated list of 200 vegetables high in protein.
High Protein Vegetables List
-
 1. Lima Beans + Add
1. Lima Beans + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories11.6g
(23% DV)6.8g
(14% DV)11.1g
(22% DV) -
 2. Soybean Sprouts + Add
2. Soybean Sprouts + Add
Protein
1 CupProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories9.2g
(18% DV)13.1g
(26% DV)21.5g
(43% DV) -
 3. Green Peas + Add
3. Green Peas + Add
Protein
1 CupProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories8.6g
(17% DV)5.4g
(11% DV)12.8g
(26% DV) -
 4. Spinach + Add
4. Spinach + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories5.3g
(11% DV)3g
(6% DV)25.8g
(52% DV)More Dark Leafy Greens High in Protein
- 5g (10% DV) per cup of cooked collard greens
- 3.5g (7% DV) per cup of cooked mustard greens
- 3.5g (7% DV) per cup of cooked Swiss chard
- 2.5g (5% DV) per cup of cooked kale
Note: Cooking reduces the water content of the greens, allowing you to eat more greens and protein per cup.
-
 5. Sweet Corn + Add
5. Sweet Corn + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories4.7g
(9% DV)3.3g
(7% DV)7.6g
(15% DV) -
 6. Asparagus + Add
6. Asparagus + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories4.3g
(9% DV)2.4g
(5% DV)21.8g
(44% DV) -
 7. Artichokes (Globe or French) + Add
7. Artichokes (Globe or French) + Add
Protein
in a Medium ArtichokeProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories4.2g
(8% DV)3.3g
(7% DV)13.9g
(28% DV) -
 8. Brussels Sprouts + Add
8. Brussels Sprouts + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories4g
(8% DV)2.6g
(5% DV)14.2g
(28% DV) -
 9. Mushrooms + Add
9. Mushrooms + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories3.9g
(8% DV)3.6g
(7% DV)27.5g
(55% DV)More Mushrooms High in Protein
- 4g (8% DV) per cup of cooked portobello
- 3.5g (7% DV) per cup of cooked shiitake
- 3g (6% DV) per cup of oyster mushrooms
- 2g (4% DV) per cup of morels
- 2g (4% DV) per cup of cremini
- 1.5g (3% DV) per cup of enokis
-
 10. Broccoli + Add
10. Broccoli + Add
Protein
per Cup CookedProtein
per 100gProtein
per 200 Calories3.7g
(7% DV)2.4g
(5% DV)13.6g
(27% DV)
Printable One Page Sheet
Less Common Protein Rich Vegetables
| Food | Serving | Protein |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Hubbard Squash + | 1 cup | 10% DV (5.1g) |
| 2. Dried Seaweed (Spirulina) + | 1 tblsp | 8% DV (4g) |
| 3. Bamboo Shoots + | 1 cup | 8% DV (3.9g) |
| 4. Jute Potherb + | 1 cup | 6% DV (3.2g) |
| 5. Pak-Choi (Bok Choy) + | per cup cooked | 5% DV (2.7g) |
| 6. Pumpkin Leaves + | 1 cup | 4% DV (1.9g) |
| 7. Broccoli Raab (Rapini) + | per cup raw | 3% DV (1.3g) |
From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Protein
- Foods Low in Protein
- Vegetables High in Protein
- Fruits High in Protein
- Vegetarian Foods High in Protein
- Nuts High in Protein
- Grains High in Protein
- Beans High in Protein
- Dairy High in Protein
- Breakfast Cereals High in Protein
- Fast Foods High in Protein
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
Simplify Nutrition Tracking with MyFoodData!
Speedy Tools and Detailed Data FREEEasily analyze your meals to find the best foods for your goals.
✅ Use our recipe nutrition calculator and nutrition comparison tool.
✅ Access expert nutrition data tools and in-depth articles.
✅ Log foods and organize your recipes with a free account.


 Next ➞
Next ➞
