Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin D

Vitamin D is an essential vitamin required by the body for the absorption of calcium, bone development, immune functioning, and alleviation of inflammation. (1,2,3)
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a weakened immune system, increased cancer risk, poor hair growth, and osteomalacia. (4,5,6)
Excess vitamin D can cause the body to absorb too much calcium, increasing the risk of kidney stones. (7,8)
The current daily value (DV) for vitamin D is 20 mcg (micrograms) (800IU) per day and the toxicity threshold is thought to be 250 to 1000 mcg/day. (9,10) Sometimes vitamin D values are given in IU (International Units). When this is the case remember that 1mcg=40IU for Vitamin D. (9)
Vitamin D is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight and is therefore called the sunshine vitamin. Sun exposure (dermal synthesis) is the primary source of vitamin D for most people. (11) Depending on the season and where you live, sunlight may not help your body create enough vitamin D. Further, elderly people often do not synthesize as much vitamin D. (12)
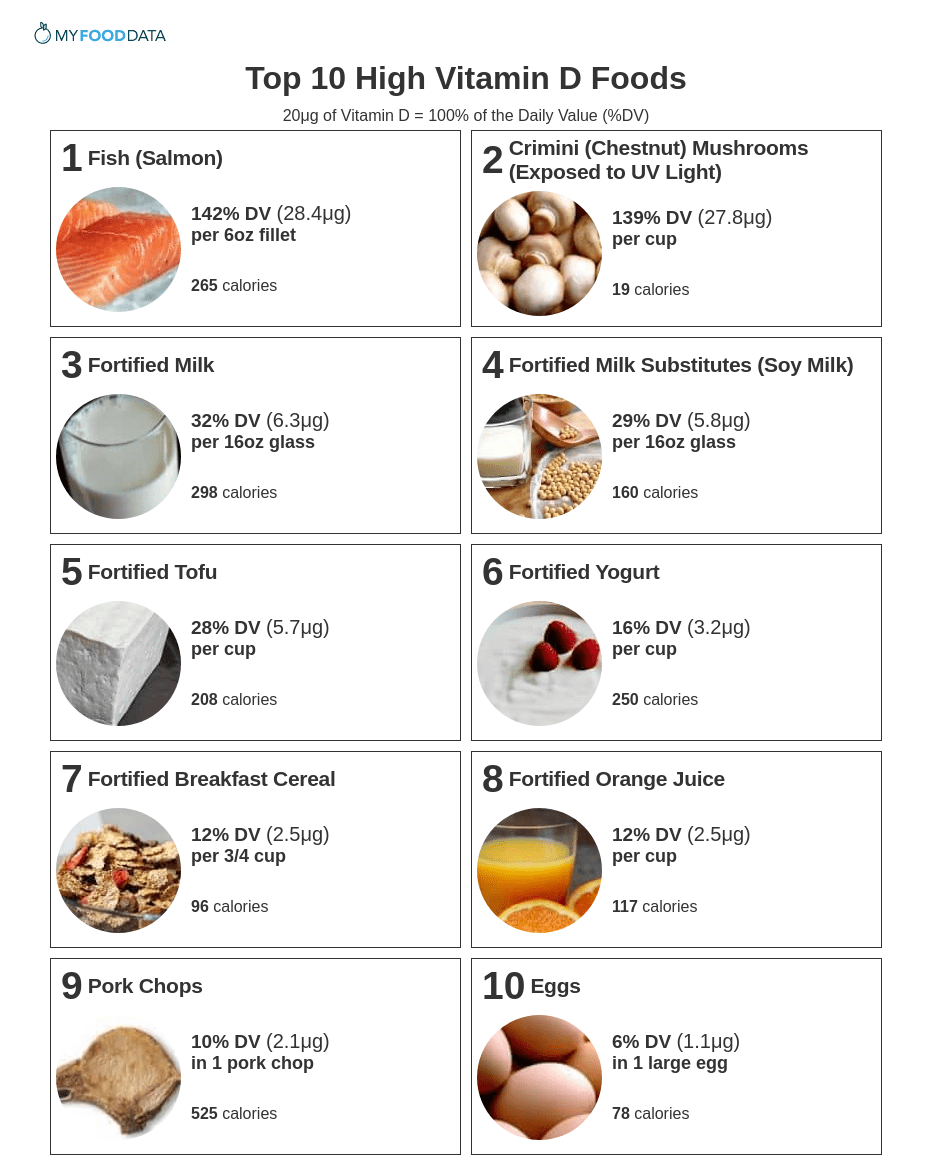
Vitamin D is fat-soluble, which means you need to eat fat to absorb it. Foods high in vitamin D include fish, mushrooms exposed to sunlight, fortified milk, fortified milk substitutes, fortified tofu, fortified yogurt, fortified breakfast cereals, fortified orange juice, pork chops, and eggs.
Vitamin D is not naturally found in many foods which is why so many foods are fortified with vitamin D. This means that vitamin D has been added to various foods for the benefit of the general public. Foods that are fortified with vitamin D also tend to be high in calcium.
Below is a list of the top 10 foods highest in vitamin D by common serving size. For more see the lists of foods high in vitamin D2, vitamin D3, and the nutrient ranking of 200 foods high in vitamin D.
- Introduction
- High Vitamin D Foods
- Printable
- Foods High in Vitamin D2
- Foods High in Vitamin D3
- How much Vitamin D Do You Need Everyday?
- Absorption of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D & Supplements
- Vitamin D in Fruits and Vegetables
- Vitamin D and Bone Pain
- Vitamin D and Muscle Weakness
- Lists By Food Group
- References
High Vitamin D Foods
-
 1. Fish (Salmon) + Add
1. Fish (Salmon) + Add
Vitamin D
per 6oz FilletVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories28.4mcg
(142% DV)16.7mcg
(84% DV)21.4mcg
(107% DV)More Fish High in Vitamin D
- 91% DV in 3oz of canned salmon
- 87% DV per cup of smoked whitefish
- 71% DV per 3oz swordfish fillet
- 67% DV in a 3oz rainbow trout fillet
- 36% DV per cup of canned sardines
- 31% DV in 6oz tilapia fillet
- 25% DV per 3oz halibut fillet
See all fish high in vitamin D.
-
 2. Crimini (Chestnut) Mushrooms (Exposed to UV Light) + Add
2. Crimini (Chestnut) Mushrooms (Exposed to UV Light) + Add
Vitamin D
per CupVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories27.8mcg
(139% DV)31.9mcg
(160% DV)290mcg
(1450% DV)More Mushrooms Exposed to Sunlight High in Vitamin D
- 122% DV per cup of portabella mushrooms
- 98% DV per cup of maitakes
- 92% DV per cup of white button mushrooms
- 17% DV per cup of morels
- 14% DV per cup of chantarelles
- 5% DV per cup of shiitakes
Mushrooms create vitamin D from sunlight much like our bodies. Placing any mushroom under the sun for 20 minutes will boost its vitamin D level.
See the list of vegetables (mushrooms) high in vitamin D.
-
 3. Fortified Milk + Add
3. Fortified Milk + Add
Vitamin D
per 16oz GlassVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories6.3mcg
(32% DV)1.3mcg
(7% DV)4.3mcg
(21% DV)More Dairy High in Vitamin D
- 29% DV per 16oz glass of low-fat milk
- 17% DV per 1/4 cup of dehydrated milk
- 16% DV per 8oz cup of buttermilk
- 4% DV per 1/4 cup of queso fresco
See all dairy foods high in vitamin D.
Note: Milk in the US is fortified with vitamin D, but does not contain significant amounts of vitamin D naturally. Therefore, milk from other countries may not be a good source of vitamin D.
-
 4. Fortified Milk Substitutes (Soy Milk) + Add
4. Fortified Milk Substitutes (Soy Milk) + Add
Vitamin D
per 16oz GlassVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories5.8mcg
(29% DV)1.2mcg
(6% DV)7.3mcg
(36% DV)Other Fortified Milk Substitutes High in Vitamin D
- 26% DV per 16oz glass of almond milk
- 24% DV per 16oz glass of rice milk
- 24% DV per 16oz glass of coconut milk
-
 5. Fortified Breakfast Cereal + Add
5. Fortified Breakfast Cereal + Add
Vitamin D
per 3/4 CupVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories2.5mcg
(12% DV)8.3mcg
(42% DV)5.2mcg
(26% DV)See the list of Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin D.
-
 6. Fortified Tofu + Add
6. Fortified Tofu + Add
Vitamin D
per CupVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories5.7mcg
(28% DV)2.5mcg
(13% DV)5.4mcg
(27% DV)See the list of Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin D.
-
 7. Fortified Yogurt + Add
7. Fortified Yogurt + Add
Vitamin D
per CupVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories3.2mcg
(16% DV)1.3mcg
(7% DV)2.5mcg
(13% DV)Yogurt is also high in calcium.
See all dairy foods high in vitamin D.
Note: Dairy products in the US are fortified with vitamin D, but do not contain significant amounts of vitamin D naturally. Therefore, dairy foods from other countries may not be a good source of vitamin D.
-
 8. Fortified Orange Juice + Add
8. Fortified Orange Juice + Add
Vitamin D
per CupVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories2.5mcg
(12% DV)1mcg
(5% DV)4.3mcg
(21% DV)Note: A cup of orange juice contains up to 20 grams of sugar.
-
 9. Pork Chops + Add
9. Pork Chops + Add
Vitamin D
in 1 Pork ChopVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories2.1mcg
(10% DV)1mcg
(5% DV)0.8mcg
(4% DV)Other Pork Products High in Vitamin D
- 11% DV per 3oz of spare ribs
- 6% DV in 1 cup of lean ham
- 6% DV per 3oz of pepperoni
- 5% DV in a 3oz bratwurst
See all meats high in vitamin D.
-
 10. Eggs + Add
10. Eggs + Add
Vitamin D
in 1 Large EggVitamin D
per 100gVitamin D
per 200 Calories1.1mcg
(6% DV)2.2mcg
(11% DV)2.8mcg
(14% DV)- 20% DV in 1 cup of scrambled eggs
- 15% DV in 1 cup of chopped hard-boiled eggs
- 5% DV in a single egg yolk
Printable One Page Sheet
Foods High in Vitamin D2
| Food | Serving | Vitamin D |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Portobellos (Exposed To Sun/UV) + | per cup diced | 79% DV (15.9mcg) |
| 2. Fortified Soy Milk + | per 16oz glass | 29% DV (5.8mcg) |
| 3. Morel Mushrooms + | per cup | 17% DV (3.4mcg) |
| 4. Fortified Almond Milk + | per cup | 12% DV (2.4mcg) |
| 5. Fortified Rice Milk + | per cup | 12% DV (2.4mcg) |
| 6. Shiitake Mushrooms + | per cup | 5% DV (1mcg) |
| 7. Oyster Mushrooms + | per cup | 3% DV (0.6mcg) |
| 8. White Button Mushrooms + | per cup | 2% DV (0.3mcg) |
Foods High in Vitamin D3
| Food | Serving | Vitamin D |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Salmon + | per 6oz fillet | 142% DV (28.4mcg) |
| 2. Rainbow Trout + | per 5oz fillet | 67% DV (13.5mcg) |
| 3. Herring + | per 5oz fillet | 39% DV (7.7mcg) |
| 4. Canned Sardines + | per cup drained | 36% DV (7.2mcg) |
| 5. Whole Milk + | per 16oz glass | 32% DV (6.3mcg) |
| 6. Tilapia + | per 6oz fillet | 31% DV (6.3mcg) |
| 7. Low-Fat and Skim Milk + | per 16oz glass | 29% DV (5.9mcg) |
| 8. Fortified Orange Juice + | per cup | 12% DV (2.5mcg) |
| 9. Roasted Pork Ribs + | per rack | 12% DV (2.5mcg) |
| 10. Canned Tuna + | per 3oz | 9% DV (1.7mcg) |
How much Vitamin D Do You Need Everyday?
The daily value (%DV) for vitamin D is 20mcg (800IU) and is a general target intended for most people. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) shows specific targets by age and gender. The RDA for vitamin D is between 15-20mcg (600-800IU) for most people.
| Life Stage | RDA |
|---|---|
| Children | |
| 1-8 years old | 15mcg (600IU) |
| Males | |
| 9-70 years old | 15mcg (600IU) |
| 70+ years old | 20mcg (800IU) |
| Females | |
| 9-70 years old | 15mcg (600IU) |
| 70+ years old | 20mcg (800IU) |
| Pregnancy | |
| 14-50 years old | 15mcg (600IU) |
| Lactation | |
| 14-50 years old | 15mcg (600IU) |
How Can I Increase Absorption of Vitamin D?
- Consuming vitamin D with fat or fatty foods can boost absorption by 11-50%. (13)
- Consuming vitamin D with a large meal increases absorption by 50%. (14)
- Magnesium plays a critical role in the activation and use of vitamin D in the body. (15) People who consume magnesium along with vitamin D display higher blood concentrations of vitamin D. (16)
Should I Supplement With Vitamin D?
Due to public health needs, vitamin D is added to an array of foods including milk, milk substitutes (soymilk), and orange juice. So to a certain extent, everyone consumes vitamin D supplements.
However, research continues to show the health benefits of good vitamin D levels. This includes the prevention of autoimmune disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, depression, dementia, infectious diseases, and musculoskeletal decline. As such, a supplement of 25mcg (1000IU) - 50mcg (2000IU) can be beneficial in certain populations. (17)
Vitamin D overdose is also a concern. Unless advised by a doctor, do not take more than 100mcg (4000IU) per day. Over time, overconsumption of vitamin D increases the risk of hypercalcemia and kidney stones. (8)
Taking supplements is a personal choice. Given adequate exposure to sun and a healthy diet made up of foods containing vitamin D, supplements may not be necessary. If you are concerned, ask your healthcare provider for a blood test to check your levels of vitamin D.
What Fruits and Vegetables are High in Vitamin D?
Vegetables high in vitamin D include mushrooms which have been exposed to sunlight. Other vegan foods high in vitamin D include fortified soy products like tofu, soy milk, and soy yogurt, fortified cereals, and fortified juices.
Unfortunately, no fruits are high in vitamin D, and fortified orange juice is currently the only fruit product commonly sold with vitamin D.
Does vitamin D Deficiency Cause Bone Pain?
Does Vitamin D Deficiency Cause Muscle Weakness?
Muscle weakness is a notable symptom of severe vitamin D deficiency (20), and even mild muscle weakness can be observed in people with vitamin D levels below 40 nmol/L.
For people with levels below 40 nmol/L, supplementing with 800-1000IU a day is enough to improve muscle performance, and also to reduce the risk of falls. (20,21)
From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Vitamin D
- Foods Low in Vitamin D
- Vegetarian Foods High in Vitamin D
- Dairy High in Vitamin D
- Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin D
- Fast Foods High in Vitamin D
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Ferrari S. Calcium and vitamin D: skeletal and extraskeletal health Rev Med Suisse. 2007 Jun 13;3(115):1515-6, 1518-20. 17682795
- Gunton JE, Girgis CM, Baldock PA, Lips P. Vitamin D, muscle and bone: Integrating effects in development, aging and injury Bone. 2015 Nov;80:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.029. Epub 2015 Mar 6. 25745883
- Kamen DL, Tangpricha V. Vitamin D and immune function J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 May;88(5):441-50. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0590-9. Epub 2010 Feb 1. 20119827
- Hernigou P, Sitbon J, Dubory A, Auregan JC. Vitamin D: part II; cod liver oil, ultraviolet radiation, and eradication of rickets Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1755-1771. doi: 10.1007/s00264-019-04334-w. Epub 2019 Apr 29. 31037319
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Dec;80(6 Suppl):1678S-88S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1678S. 15585788
- Gerkowicz A, Chyl-Surdacka K, Krasowska D, Chodorowska G. Role of vitamin D in hair loss: A short review Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 7;18(12):2653. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122653. 29215595
- Johri N, Jaeger P, Ferraro PM, Shavit L, Nair D, Robertson WG, Gambaro G, Unwin RJ. Vitamin D, Hypercalciuria and Kidney Stones Urolithiasis. 2017 Dec;45(6):535-543. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0954-x. Epub 2016 Dec 16. 27981376
- Chevalley T, Brandi ML, Cashman KD, Cavalier E, Harvey NC, Maggi S, Cooper C, Al-Daghri N, Bock O, Bruyère O, Rosa MM, Cortet B, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Cherubini A, Dawson-Hughes B, Fielding R, Fuggle N, Halbout P, Kanis JA, Kaufman JM, Lamy O, Laslop A, Yerro MCP, Radermecker R, Thiyagarajan JA, Thomas T, Veronese N, de Wit M, Reginster JY, Rizzoli R. Vitamin D supplementation: upper limit for safety revisited? Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 Nov;34(11):2603-2623. doi: 10.1007/s40520-022-02279-6. Epub 2022 Oct 26. 36287325
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
- Aloia JF. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Oct;96(10):2987-96. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0090. Epub 2011 Jul 27. 21795456
- Holick MF. Factors that influence the cutaneous synthesis and dietary sources of vitamin D Fed Proc. 1987 Apr;46(5):1876-82. 3030826
- Holick MF. Aging decreases the capacity of human skin to produce vitamin D3 Fed Proc. 1987 Apr;46(5):1876-82. 3030826
- Dawson-Hughes B, Harris SS, Palermo NJ, Ceglia L, Rasmussen H. Dietary fat increases vitamin D-3 absorption J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Aug;28(8):1778-83. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1896. 23427007
- Leidig-Bruckner G, Roth HJ, Bruckner T, Lorenz A, Raue F, Frank-Raue K. Taking vitamin D with the largest meal improves absorption and results in higher serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D Osteoporos Int. 2011 Jan;22(1):231-40. doi: 10.1007/s00198-010-1214-5. Epub 2010 Jun 17. 20556359
- Mazokopakis EE, Papadomanolaki MG. Role of Magnesium in Vitamin D Activation and Function J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2018 Dec 1;118(12):772-773. doi: 10.7556/jaoa.2018.167. 30476986
- Dall RD, Cheung MM, Shewokis PA, Altasan A, Volpe SL, Amori R, Singh H, Sukumar D. The effect of combined magnesium and vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D status, systemic inflammation, and blood pressure: A randomized double-blinded controlled trial Nutr Res. 2023 Feb;110:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2022.12.005. Epub 2022 Dec 22. 36640582
- Cannell JJ, Hollis BW. Vitamin D supplementation: what's known, what to do, and what's needed Altern Med Rev. 2008 Mar;13(1):6-20. 18377099
- Heidari B, Shirvani JS, Firouzjahi A, Heidari P, Hajian-Tilaki KO. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with tibial bone pain and tenderness. A possible contributive role Int J Rheum Dis. 2010 Oct;13(4):340-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01561.x. Epub 2010 Aug 16. 21199469
- Babaei M, Esmaeili Jadidi M, Heidari B, Gholinia H. Association between nonspecific skeletal pain and vitamin D deficiency Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Apr;21(4):788-795. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13253. Epub 2018 Jan 5. 29314669
- Dawson-Hughes B. Vitamin D and muscle function Proc Nutr Soc. 2012 Feb;71(1):46-9. doi: 10.1017/S0029665111003260. Epub 2011 Nov 1. 22040926
- Lips P. Vitamin D and muscle function Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006 Sep;92(1):4-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.02.016. Epub 2006 Feb 28. 16563471
Simplify Nutrition Tracking with MyFoodData!
Speedy Tools and Detailed Data FREEEasily analyze your meals to find the best foods for your goals.
✅ Use our recipe nutrition calculator and nutrition comparison tool.
✅ Access expert nutrition data tools and in-depth articles.
✅ Log foods and organize your recipes with a free account.


 Next ➞
Next ➞
